Bring Finite Element Analysis into your tolerance analysis system to account for flexible materials, parts, heat, force, and gravity
Traditional variation analysis methods are considered to be "rigid-body" or "non-compliant" modeling; meaning, that every part
While this might be the case with a few machined components, most commodities and materials like sheet metal, plastics, aluminum, etc. can be heavily influenced
3DCS FEA Compliant Modeler, an add-on module to the 3DCS software solutions, utilizes FEA methods to accurately simulate variation of compliant parts and assemblies within the 3D Variation Analysis model.










Combine traditional tolerance analysis with FEA analysis to determine the impact of clamping, force, gravity and heat on your parts
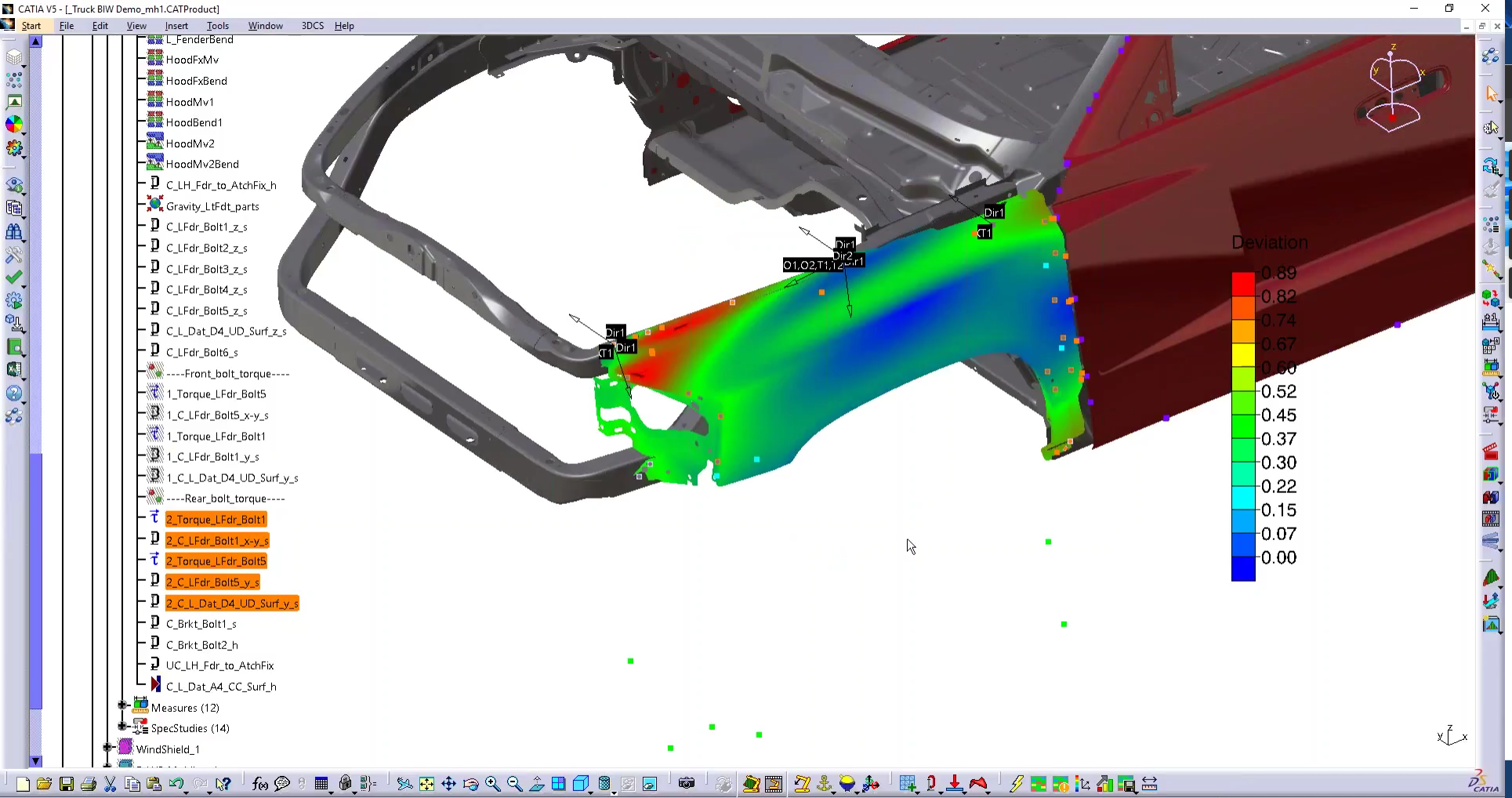
When welding, bolting, riveting or assembling parts, the order and the process can have as much of an effect on final results as the parts themselves. Riveting can stretch aircraft aluminum skin, assembling can bend and cause spring back, and bolting can warp materials. Simulate, test and determine the best order of operations and the impact these processes will have on your parts.
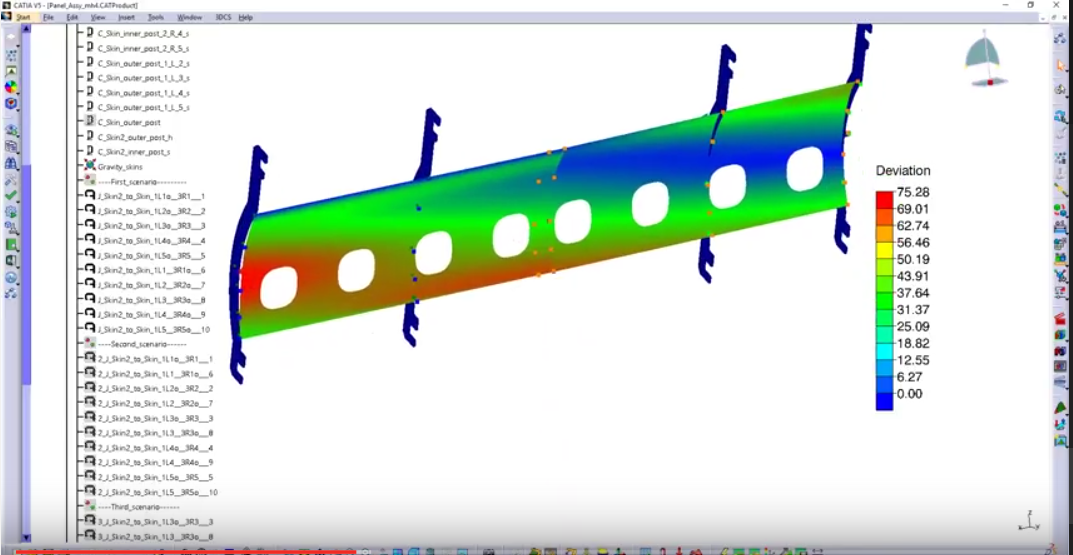
See how the material reacts to forces in the model and alters the amount of variation inherent in the system.
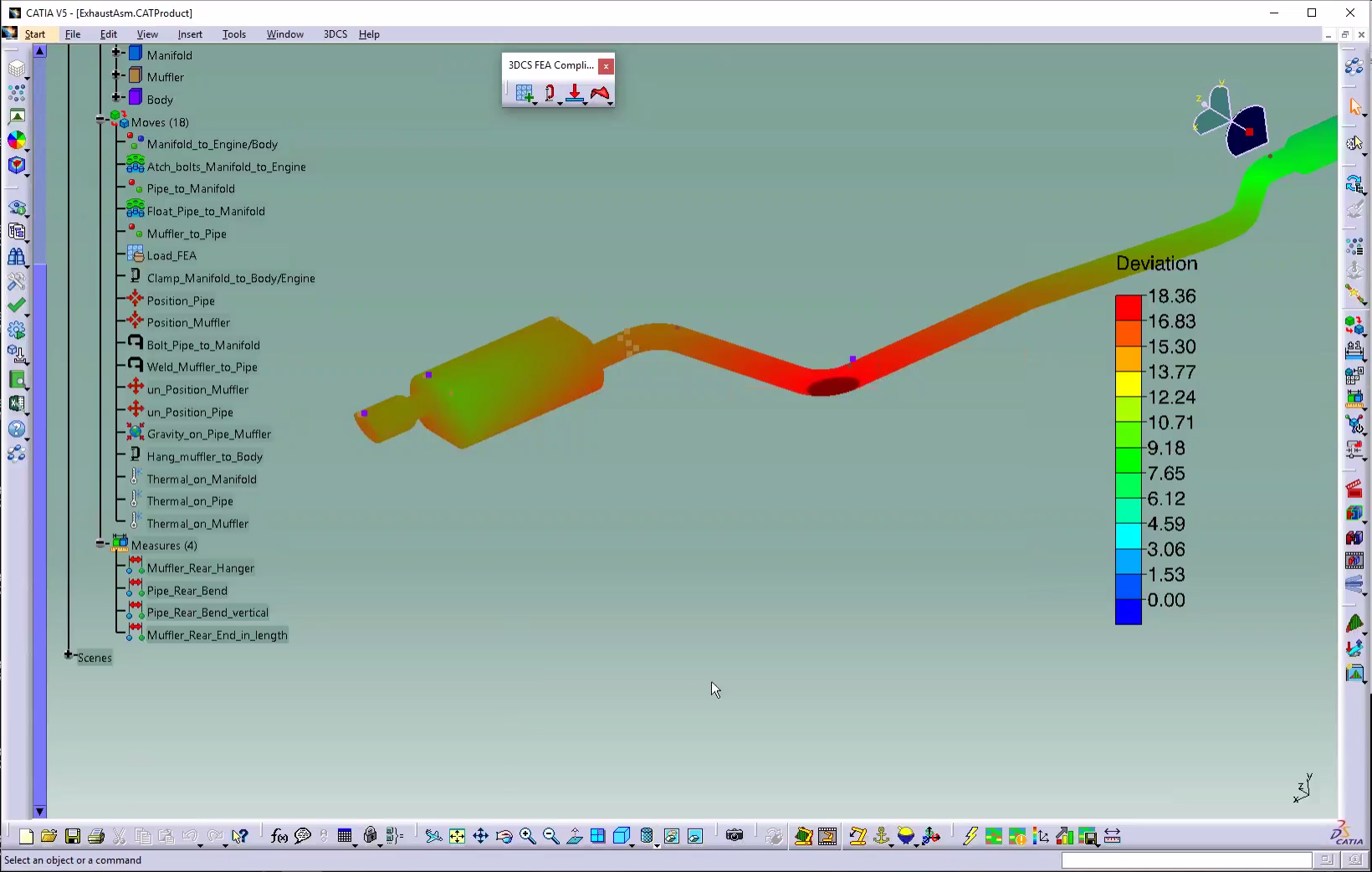
Use rubber bushings and washers. See how rivets and bolts affect aluminum sheets. Find out how environmental and operational heat deforms components.
Advanced applications for optimization will are covered in this webinar on-demand.
When flexible parts are in an assembly, or the effects of gravity and force affect the final assembly, 3DCS FEA Compliant Modeler can create more accurate results.
Learn More →
Create series of clamps and welds, and then release the clamps to understand how the parts will deform.
Our CSS classes help to add spacing, justify text, hide elements at various screen sizes and much more.
Learn More →

When welding, bolting, riveting or assembling parts, the order and the process can have as much of an effect on final results as the parts themselves. Riveting can stretch aircraft aluminum skin, assembling can bend and cause spring back, and bolting can warp materials. Simulate, test and determine the best order of operations and the impact these processes will have on your parts.
Determine how welding, bolting and connecting parts affects the dimensional characteristics of your product. Find out how the use of flexible materials like aluminum changes the way your product reacts to manufacturing processes.
Parts sag from their weight, or expand when welded or in use. Automotive hoods flex and bend to product springback force, and aluminum skin in aircraft stretches and distorts when riveted. Determine how these processes and forces affect your product's quality, and account for it through process change, tolerance changes or tooling.
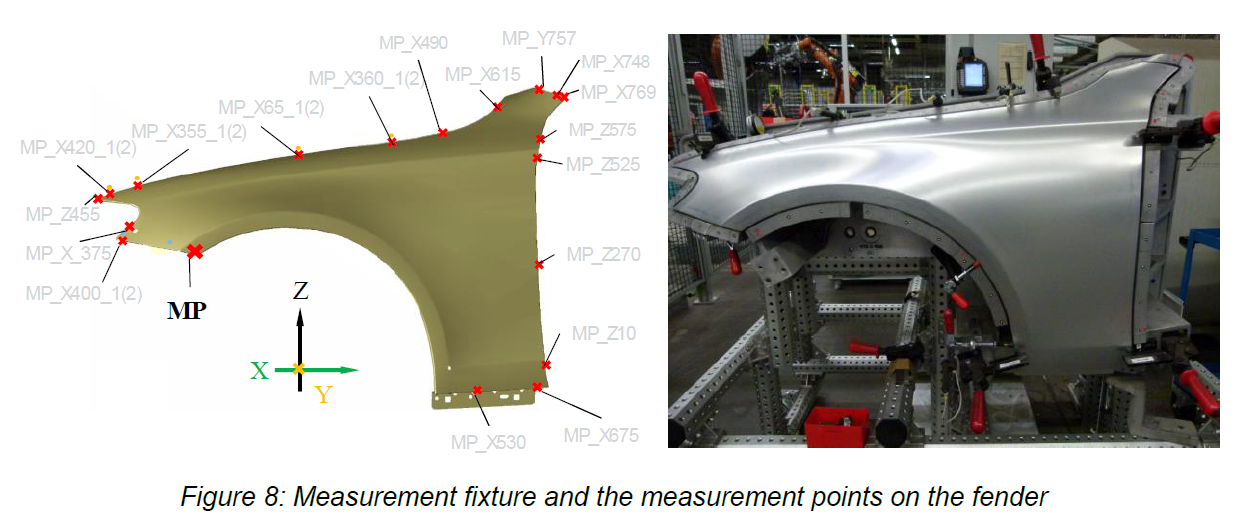
Determine the changes to your product based on constraints, forces and operations.
Test different assembly sequences and processes such as welding, riveting, bolting and clamping to find optimal placements, order of operation and the effect on the assembly.